“Most important cause why many of the merchandise fail is because of lack of product-market match.” ~Dan Olsen
Product-Market Match is inarguably one of many foremost elements deciding on product success or failure. However what product-market match is, precisely? And the right way to obtain it?
This text is impressed by the e-book The Lean Product Playbook: Tips on how to Innovate with Minimal Viable Merchandise and Speedy Buyer Suggestions by Dan Olsen and goals to explain two important ideas described within the e-book, particularly the Product-Market Match Pyramid and the Lean Product Course of that goals to assist us obtain that match.
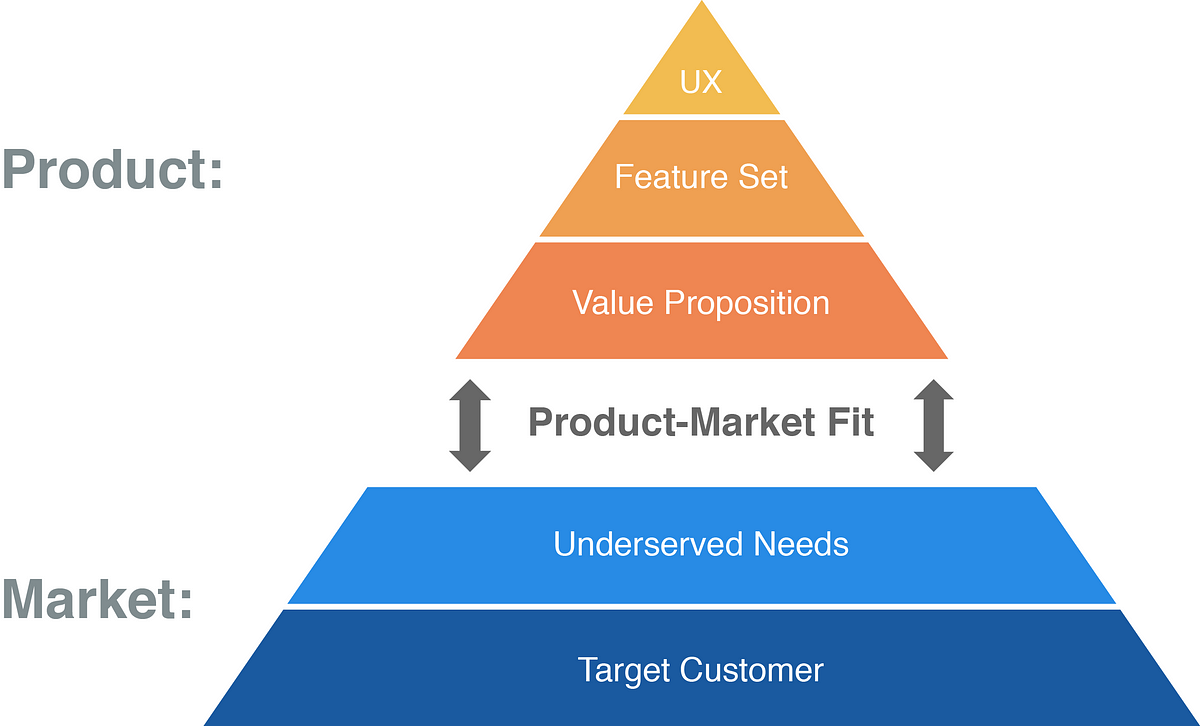
Allow us to begin by defining the product, the market and the product-market match.
The market consists of all the present and potential clients that share a standard want. For instance, all of the individuals within the UK desirous to get into Tech. It’s usually counted as both the overall variety of clients or the overall income generated by these clients.
The market can include two essential elements — goal buyer and underserved wants. Goal clients are your persona — it’s the kind of buyer you wish to go after. That buyer will need to have some underserved must be a viable market — in any other case, there’s no level getting into a “market” the place customers are delighted with current options.
The product’s basis is a considerable Worth Proposition. It defines which underserved wants the product goals to fulfill and the way it’s higher than rivals. Based mostly on this basis, we will outline a characteristic set — what options your product must materialise the Worth Proposition. The UX is the ultimate impact — how properly your product realises that worth by the characteristic set — how intuitive, accessible and fulfilling it’s to make use of.
The product-market match measures how properly your product (high 3 layers) fulfill the market (backside two layers) with relation to different options accessible available on the market.
Now that we outlined the product-market match let me stroll you thru the six-step means of attaining the match.
Extra Readings
We begin with defining our goal group. If you’re doing it for the primary time for a given product, keep in mind one factor — it’s a speculation.
“Your product is the bait that you just put on the market, and the fish that you just catch is your goal buyer. Typically you catch the kind of fish you had been going after, and generally you catch a distinct sort of fish. You may develop hypotheses about your goal market, however you received’t actually know who your clients are till you throw your hook into the water and see what sort of fish chew. After getting a product or a prototype to point out clients, then you possibly can achieve readability in regards to the goal market you’re attracting.” ~Dan Olsen
Regardless that you’ll know what fish bites solely after you throw your hook on the market, it’s important to begin with one thing, don’t you?
You most likely begin with some high-level hypotheses of the issue you wish to remedy. Based mostly on that speculation, you would specify your market phase utilizing a number of segmentations strategies. The most well-liked segmentation classes are:
- Demographics (e.g. gender, age, marital standing, revenue, training)
- Psychology (attitudes, opinions, values, pursuits)
- Behaviour (e.g. Mothers that publish footage of their infants on Instagram each week)
- Wants (individuals which are fearful about their infants at evening)
Whereas demographics and psychology is likely to be useful, behaviours and wants are what it is best to give probably the most consideration to.
After preliminary market segmentation, you’d wish to create your first speculation of a Persona. To maintain it easy:
- Discuss to potential clients from the market phase you outlined, attempt to perceive them, their traits, ache factors, wants. Good personas are based mostly on analysis, not needs.
- You may must create a couple of persona to get higher readability of your goal group. It’s higher to distinguish 1–3 completely different personas than one based mostly on “common”.
- Do not forget that your Purchaser (an individual who pays for the product) is likely to be a distinct persona than your person (an individual who makes use of the product).
Extra Readings
Now that you’ve a speculation of your goal group, it’s time to go on the market and speak together with your potential customers. There are numerous approaches to person analysis, however the indeniable winner at this stage is dwell 1–1 dialog.
Your purpose at this stage is, because the title of the step suggests, discovering areas which are useful to customers (wants) and but not totally happy by current options (underserved).
The important factor to recollect right here is that persons are normally unskilled in describing their issues. It is likely to be simpler to collect insights from speaking about current options — why do they use them? What’s lacking there? Why is that a problem?
After some digging, it is best to have some hypotheses about potential underserved wants. Now you possibly can attempt to validate them. Some useful questions for preliminary want validation:
- What does this assertion imply to you?
- If we had been to ship profit X, how useful would that be to you? Why?
Alternative Rating
Now that you’ve some preliminary assumptions, how do you determine which wants do you have to give attention to? One of many strategies is judging Significance vs Satisfaction Framework.
It’s a easy but compelling framework. Briefly, you ask your person’s how Necessary a specific want is for them and the way happy they’re with current options available on the market.
That is the place quantitative analysis shines — you need a number of information. One of many approaches is to ask numerous customers to charge significance and satisfaction on scales resembling 1–5 or 1–7, and if there’s a distinction between the 2, that’s your alternative rating.
Given the drawbacks of straightforward subtraction, right here’s a barely extra refined components for calculating Alternative Scores.
Alternative Rating = Significance + Most (Significance — Satisfaction, 0)
Alternative Rating helps you notice these options with excessive significance and low satisfaction, and people wants are most value pursuing.
The Kano Mannequin
One other necessary side in defining the underserved buyer wants you to wish to goal classifying them into three classes:
- Should-haves: Components that don’t carry extra satisfaction, however an absence of them brings dissatisfaction. As soon as the necessity is happy, rising the must-have doesn’t add any extra worth.
- Efficiency: Core wants — within the eyes of your clients, these are the important points of the merchandise. “Extra is healthier” method.
- Delighters: Space of innovation — customers don’t count on them, so lack of them doesn’t trigger any dissatisfaction, however they’ll generate a number of satisfaction and offer you a aggressive edge.
To be extra tangible, let’s check out automotive instance:
Should-have:
- Seatbelt — you wouldn’t wish to trip a automotive with no seatbelts, however when you fulfill the fundamental want (one seatbelt per seaTips & Tips
- Kano mannequin is transferring!
- In prioritisation, embrace not less than 1 delighter.t), including extra seatbelts received’t add extra worth)
Efficiency options:
- Pace — the higher the efficiency of the automotive, the extra aggressive it’s available on the market.
- Gas consumption — the much less gasoline a automotive consumes, the extra aggressive it’s available on the market.
Delighters:
- Cupholders* — within the 80s, vehicles didn’t have cupholders, so after they had been added, they added model new, unanticipated worth to clients.
*these days, cupholders will not be delighters anymore. I used this instance to show one essential precept:
“Yesterday’s delighters turn into at this time’s efficiency options and tomorrow must-haves.” ~Dan Olsen
Extra Readings
You need to have already got:
- Hypotheses about desired advantages.
- Alternative rating for every of the advantages.
- Classification of those advantages.
The subsequent step is to determine what you might be not going to do.
“Folks suppose focus means saying sure to the factor you’ve acquired to give attention to. However that’s not what it means in any respect. It means saying no to the hundred different good concepts that there are. It’s a must to choose fastidiously. I’m as happy with the issues we haven’t achieved because the issues I’ve achieved. Innovation is saying no to 1,000 issues.” — Steve Jobs.
You may’t have all of it, particularly if you’re nonetheless looking for the product-market match. Since must-haves are non-negotiable, they don’t carry any extra satisfaction. Thus, the worth proposition consists of your alternative of efficiency options and delighters.
Worth Proposition = Efficiency Options + Delighters
Defining MVP means deciding which efficiency options and delighters you’ll give attention to and which you select to not give attention to. Right here it’s necessary to recollect one essential side — individuals will choose your product in relation to different options accessible out there, and your Worth Proposition ought to replicate that.
It will be greatest to attempt to predict how your rivals Worth Proposition will appear like sooner or later and plan your technique based mostly on that.
Wanting on the desk above, we will spot the Worth Proposition based mostly on the Kano Mannequin. Our sport is to dominate in efficiency profit 3, and in the long term, compete in efficiency profit 1. To take action, we determine to disregard efficiency profit 2. We additionally differentiate ourselves by pursuing a distinct set of delighters. Our aggressive benefit lies in efficiency profit 3, delighter two and delighter 4, and that’s our price proposition.
Extra Readings
The subsequent step is to outline what options you wish to embrace in your MVP. Easy course of for that’s:
- Brainstorm doable options contributing to your worth proposition.
- Categorise them by wants/advantages recognized in Step 2.
- Select high 1–3 options per profit.
To correctly prioritise which options are probably the most value pursuing, it is best to calculate effort vs worth.
Within the case of digital merchandise, your growth workforce might be one of the best supply of effort estimation, whether or not in time-needed, story factors, t-shirt sizing or some other technique.
The worth is a extra difficult one. Relying in your particular circumstances, you possibly can calculate every characteristic’s detailed Return on Funding or estimate it on a scale of 1–5 based mostly in your greatest assumptions.
You may prioritise a speculation about effort and worth based mostly on that — pursuing highest-value lowest-effort options first. You don’t have to incorporate all elements without delay, particularly that you just haven’t validated your assumptions but. The rule of thumb is that the v1 of your MVP ought to have one thing that clients discover superior to different merchandise.
Extra Readings
Now it’s time to construct your MVP. There are numerous approaches for that; allow us to begin with categorising MVP checks by sorts.
Advertising checks vs product checks
Advertising MVP checks embrace touchdown pages, movies, advert campaigns, crowdfunding, and so forth. General, you don’t construct any prototype of the product, simply messaging across the product. Their purpose is to gauge market pursuits and take a look at your messaging.
Product MVP checks, however, are oriented towards testing the product idea itself. It ranges from a primary wireframe, ending on a dwell product itself. The aim is to validate assumptions and achieve concrete product suggestions.
Qualitative checks vs quantitative checks
Qualitative Assessments imply deeper testing with a smaller group of customers to collect perception. They help you perceive your customers’ behaviours higher and choose if there’s match or not. They reply “Why” questions. Why customers behave in particular methods and why they like/dislike the answer.
Quantitative Assessments, however, give attention to gathering a number of information from numerous customers, usually attaining statistical significance. They offer a number of information, answering “what” and “what number of” questions, however normally with none extra perception about “why”.
The kind of MVP proper on your product enormously depends upon your explicit product imaginative and prescient, wants, price range, and confidence stage in assumptions you could have.
Person Expertise issues
Let’s not overlook in regards to the high layer of the pyramid — the UX. Your MVP have to be purposeful but additionally dependable, usable, and pleasant. In any other case, it’ll be robust to tell apart in case your customers don’t like your product as a result of lack of product-market match or just because it’s not dependable, even for them.
Extra Readings
We did to this point to create an experiment based mostly on our hypotheses, and now it’s time to validate them with clients.
There are a number of methods to conduct correct person checks, and so they enormously depend upon the kind of MVP you could have determined to pursue.
If you’re doing a product MVP take a look at (which is important sooner or later), one of the crucial glorious sources of insights is 1–1 interviews with customers.
A very powerful factor to recollect — be sure you are testing together with your goal clients outlined in Step 1; in any other case, the outcomes will probably be skewed. A well-prepared screener ought to mitigate the danger of testing with the incorrect customers.
More often than not, you take a look at three distinguish parts on the identical time.
- Usability — ease of use.
- Messaging — the message the product conveys.
- The product-market match.
It’s necessary to tell apart between them; you possibly can obtain excellent usability and have excellent messaging, but nonetheless not attain the product-market match.
Assuming that your preliminary MVP shouldn’t be but dwell product, you possibly can attempt to gauge the product-market match by asking customers:
- How useful do they discover the answer?
- Would they use the answer?
- Are they keen to pay for it?
Extra Readings
It’s unbelievable to achieve the proper product-market match in your first attempt, and even when there’s match, there’s most likely loads of room for enchancment. The Lean Product Course of proposes a barely modified product loop impressed by Lean Startup.
- Hypothesise (Step 1–3)
- Design (Step 4–5)
- Check (Step 6)
- Be taught (Step 6)
- Repeat
Should you encounter an issue — for instance, customers will not be inquisitive about your product, have a look again on the Product-Market Match pyramid and see what speculation it invalidates.
- Does the chosen characteristic set realise your Worth Proposition?
- Does your Worth Proposition actually tackle underserved wants?
- Have you ever confirmed that the wants are the precise ache factors?
- Are you continue to pursuing the identical goal group?
No matter the issue, you possibly can all the time observe it to a selected layer on the pyramid.
Now, you should determine if you wish to attempt to validate the speculation one other manner (persevere) or considerably change among the hypotheses (pivot) within the subsequent iteration.
Extra Studying
- Probably the most important concerns creating a brand new product is attaining the correct stage of product-market match.
- Product-market match is the measure of how properly your product serves the market.
- To search out product-market match, you should use a lean product course of consisting of 6 steps.
- Step 1. Begin with market segmentation and person persona. Keep in mind, it have to be based mostly on expert analysis.
- Step 2. Discuss to your goal group to find underlying wants.
- Use the Satisfaction vs Significance evaluation to seek out the alternatives to pursue.
- Distinguish between must-have, efficiency and delighter wants.
- Step 3. Resolve which wants you’ll fulfill and which you received’t.
- Customers will choose your product in relation to different options. Assume the way you’ll be completely different.
- Step 4. Take into consideration what options can realise your worth proposition and prioritise based mostly on effort vs worth evaluation.
- Step 5. Resolve in your MVP prototype.
- Advertising MVP checks are nice for testing your message and gauging customers pursuits.
- Product MVP checks are essential to validating your assumptions and studying extra about your customers.
- Qualitative checks goal to reply “why?” questions.
- Quantitative checks goal to reply “what?” and “what number of?” questions.
- By no means neglect Person Expertise. MVP shouldn’t be an excuse for poor UX.
- Step 6. Check together with your clients. The precise manner will depend upon the MVP sort you’ve determined to pursue.
- Should you haven’t but achieved product-market match, you possibly can normally map the underlying downside to some speculation on the product-market match pyramid.
- Iterate the method usually utilizing the hypothesise → design → take a look at → study suggestions loop.