To get outcomes from paid search, you’ll have to ship higher campaigns and enhance your bids, which drives prices up.
Nevertheless, growing your bids received’t at all times imply extra clicks. Finally, you’ll attain some extent the place elevated bids will solely return little to no achieve.
That is the regulation of diminishing returns at play. When operating PPC campaigns, you’re contending with this idea and plenty of different components exterior your management.
On this article, we’ll discover the regulation of diminishing returns and varied components making paid search much more demanding at present. This can enable you set higher expectations when assessing your PPC efficiency.
The regulation of diminishing returns
In economics, the regulation of diminishing returns states that as a corporation will increase its funding in a particular space, the speed of revenue generated by that funding will finally attain some extent the place it can not proceed to rise, assuming that every one different variables stay fixed.
Because of this, extra funding in that space will lead to a decreased fee of return. At a sure stage of enlargement, the return on funding that applies to extra models produced (marginal ROI) reaches a unfavorable worth.
Past this level, the entire end result will begin declining. Even when it stays constructive, it’s not as excessive as the utmost.
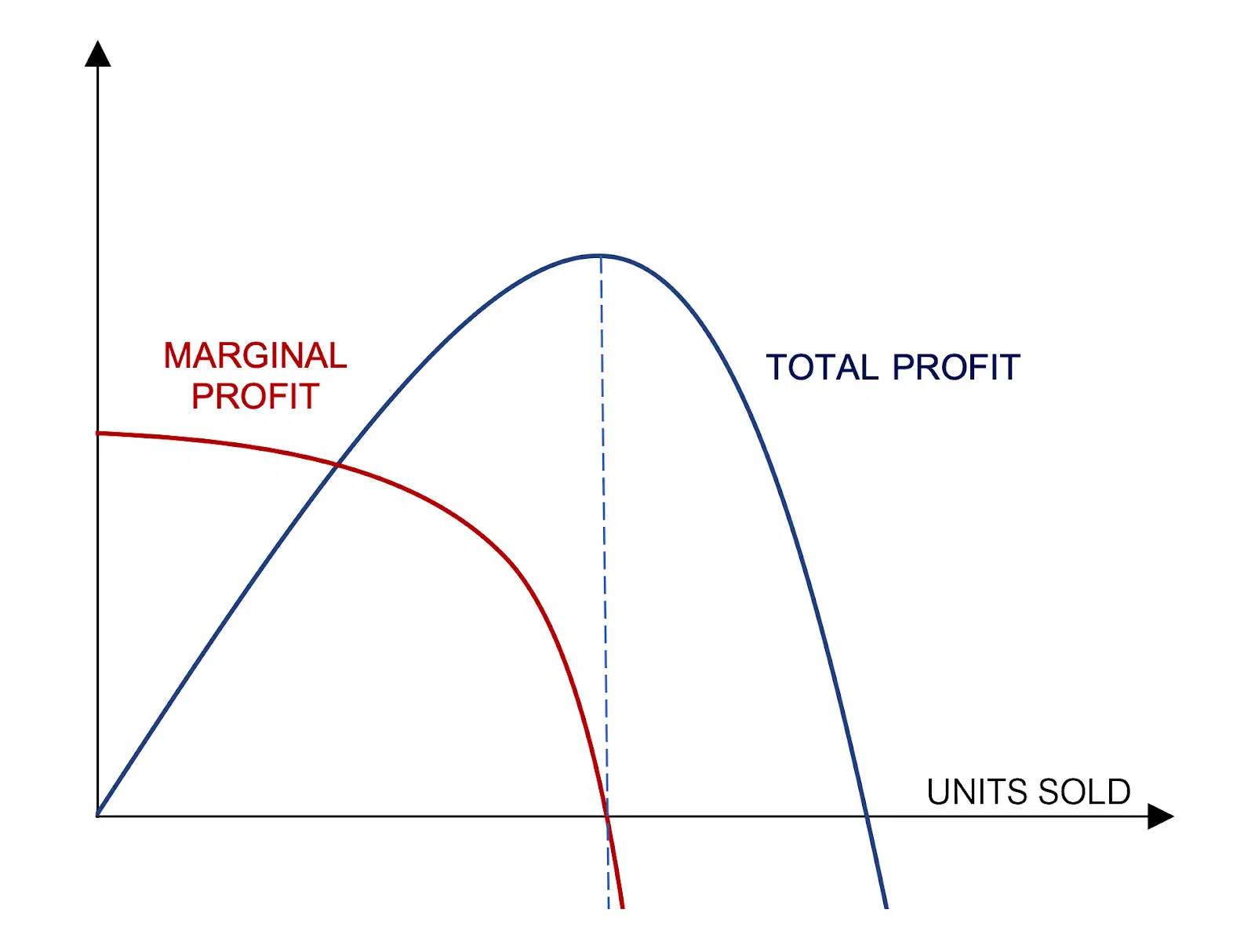

This precept highlights the significance of discovering the optimum degree of funding to maximise the general revenue. The “candy spot” is the place the marginal ROI adjustments from constructive to unfavorable, particularly the place the marginal return equals zero.
As each useful resource is restricted, we observe that the availability exhibits lowering responsiveness to the value change, and finally doesn’t matter how excessive the value is. The provision received’t be greater. This phenomenon is described because the regulation of diminishing elasticity.
Value elasticity (E) measures the responsiveness of the demand or provide to a change within the worth of an excellent or service. It’s calculated as the share change within the amount of an excellent or service demanded or equipped in response to a share change in its worth.
If the value elasticity is bigger than one, the demand or provide is claimed to be elastic, that means {that a} slight change in worth results in a comparatively bigger change within the demand or provide. If the value elasticity is lower than one, the demand or provide is claimed to be inelastic.
Get the day by day e-newsletter search entrepreneurs depend on.
Why are CPCs so excessive?
The legal guidelines of diminishing returns and elasticity apply to promoting.
To generate extra site visitors and conversions by means of PPC, it’s a must to be extra aggressive and aggressive, growing bids and, in flip, accepting greater conversion prices.
Rising value per click on (CPC), nevertheless, results in smaller and smaller will increase in site visitors. Finally, you may attain some extent when there is not any probability to get extra site visitors from a particular key phrase (i.e., if the advert ranks #1 for all searches with 100% impression share).
The regulation on diminishing returns can be mirrored within the complete price range. You’ll be able to see how these prices can change within the Google Advertisements Efficiency Planner, as proven within the illustration beneath.
Normally, the connection can be pretty easy for campaigns that aren’t beneath or overinvested. To get 10% extra site visitors, it’s good to settle for a ~10% greater conversion value or a ~10% decrease return on advert spend (ROAS).
Which means Google’s typical worth elasticity of provide (the relative ratio of site visitors enhance to CPC enhance) is 1.
Why is that this the case? If a vendor will increase their margin by 10% and loses 20% of their prospects, this operation will lead to a loss, and costs will doubtless be too excessive.
If a ten% enhance in margin solely causes 5% of shoppers to depart, the vendor will enhance their earnings, and former costs had been too low.
The purpose at which the value is most optimum for the vendor is the place a ten% enhance in margin ends in a ten% lower within the gross sales quantity, making the change impartial for earnings. In different phrases, the gross sales earnings are highest if the value elasticity of demand is 1.
For Google, the gross sales margin just about equals promoting income as a result of the variable prices of the advert impression and click on are negligible.
To maximise their earnings, they need to keep a worth elasticity of 1 – which explains how the public sale algorithm works and why this regularity exists available on the market.
Why does it value a lot?
In PPC, the pure consequence of the regulation of diminishing returns is a non-linear enhance in price range to scale the marketing campaign.
With elasticity E=1, which is typical for the market, doubling the site visitors and gross sales quantity is related to doubling the CPC, leading to a four-fold enhance in price range.
At different ranges of elasticity, these proportions can be totally different. However it’s unrealistic to assume that doubling the price range will result in doubling gross sales in a given channel.
Advertising and enterprise plans usually replicate such expectations, solely to fall by means of later. Growth is expensive, and the reality is much more bitter than this.
Google and Meta are right here to do enterprise
The price of buying a further click on (i.e., the marginal value per click on or CPCm) is sort of at all times greater than the precise CPC. By definition:
Additionally, by definition, the elasticity:
Due to this fact:
It signifies that at E=1, shopping for extra clicks is twice dearer than the present value per click on. The identical calculations apply to Efficient Income Share (ERS = Price / Income)
Advertisers profit from investing in promoting so long as the marginal value is decrease than their revenue margin (i.e., they get extra revenue by means of promoting).
When the marginal efficient income share reaches ERSm=1, promoting prices devour all the income. Additional, enlargement can have unfavorable marginal income and the entire income will begin to lower. Thus, the marketing campaign generates most complete revenue when:
That’s:
As ROAS = 1/ERS = ROI + 1, this system may be written as ROAS = 1 + 1/E or ROI = 1/E.
A easy system can outline the areas of beneath and overinvestment and the optimum degree.
If E = 1 (the standard market elasticity), the utmost complete earnings from promoting happen when ROI = 100% or ERS = 0.5.
It signifies that, on common, advertisers enhance their earnings till they spend 50% of their revenue (with out contemplating fastened prices) on PPC adverts.
In fact, specific advertisers who promote roughly aggressively could also be in a special space of elasticity than E=1. Due to this fact, the ERS/ROAS/ROI maximizing advertiser earnings can be greater or decrease.
For each $1 invested in Google search, U.S. corporations earn $2. That is how Google desires to see it, however it additionally signifies that corporations give half their earnings to those tech giants.
There is not any method round it
The legal guidelines of economics and the free market put companies in a state of affairs the place Google, Meta and different advert platforms get half their gross sales margin earlier than fastened value.
Whether or not we prefer it or not, these are the principles of promoting. Understanding how the system works makes it simpler to create lifelike enlargement plans and keep away from disappointments.
Opinions expressed on this article are these of the visitor creator and never essentially Search Engine Land. Employees authors are listed right here.